Who is a Data Scientist?
Who is a Data Scientist?
Who is a Data Scientist?
The other day, I read an article on venturebeat.com that revealed how advanced data analytics helped Obama win the 2012 presidential elections! This and more stories like Bank of America benefiting from its data-intensive technologies or Wipro putting in $30 million in a US-based data science firm or Paypal hiring data scientists, give a clear reflection that Data Scientist is the sexiest job of the 21st century as quoted by Harvard.
A data scientist is a highly skilled professional who possesses a unique combination of technical expertise, domain knowledge, and analytical acumen.
Their primary role revolves around extracting valuable insights and knowledge from large and complex datasets using various tools, programming languages, and statistical techniques.
Data scientists not only possess a strong foundation in mathematics, statistics, and computer science but also have the ability to understand business objectives and apply their findings to solve real-world problems.
For example, in the healthcare industry, a data scientist may analyze patient data to identify patterns that could lead to the early detection of certain diseases or optimize treatment plans.
By delving into large volumes of medical records and genetic data, they can uncover crucial insights that improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
In the retail sector, a data scientist might work on recommendation systems, analyzing customer behavior and purchase history to personalize product recommendations.
By leveraging machine learning algorithms, they can enhance customer satisfaction and drive higher sales by offering tailored suggestions based on individual preferences
In the financial sector, data scientists play a significant role in fraud detection and risk assessment.
By analyzing transaction data and historical patterns, they can build predictive models to detect potential fraudulent activities and assess credit risk for loan approvals, ultimately mitigating financial losses and ensuring a safer environment for customers and businesses alike.
In summary, data scientists are multidisciplinary professionals capable of translating raw data into actionable insights that have a profound impact across various industries, revolutionizing decision-making processes and driving innovation.
Their expertise in data analysis and predictive modeling allows organizations to harness the power of data, gain a competitive edge, and make well-informed decisions for a successful future.
After hearing so much about Data Science, let’s get into some basics!
What is Data Science all about?
Some call it as Civil Engineering of data, and others call it a Discipline in itself; after all, what is Data Science all about?
Data Science is a term which came into popularity by EMC2. It is a process of extracting valuable insights from “data”.
You may go through the webinar recording of “Who is a Data Scientist” where our expert has explained the topics in a detailed manner.
As we are living in the Big Data Era, Data Science is becoming a very promising field to harness and process huge volumes of data generated from various sources. Data Science is a vast discipline in itself, consisting of specialized skill-sets such as statistics, mathematics, programming, computer science and so on. Data science consists of several elements, techniques and theories including math, statistics, predictive analysis, data modelling, data engineering, data miming, and visualization.
The discipline of data science hasn’t evolved overnight. In fact, it has been there for years in the form of business analytics or competitive intelligence, but it is now only that its true potential has been realized. The main purpose of Data Science is to extract and interpret data effectively and present it in a simple, non-technical language to the end users.
Thus, Data Science is all about constructing useful information, thereby, converting it into
data-driven products!
Who is a Data Scientist?
Is he/she someone struggling with data all day and night or experimenting in his/her laboratory with complex mathematics? After all, ‘Who is a Data Scientist’?
There are several definitions available on Data Scientists. In simple words, a Data Scientist is one who practices the art of Data Science. The highly popular term of ‘Data Scientist’ was coined by DJ Patil and Jeff Hammerbacher. Data scientists are those who crack complex data problems with their strong expertise in certain scientific disciplines. They work with several elements related to mathematics, statistics, computer science, etc (though they may not be an expert in all these fields).
Data Scientists are Business Analysts or Data Analysts, with a difference!
Though the initial training or basic requirements are similar for all these disciplines, Data Scientists require:

Whether an agricultural scientist wants to know the percentage increase in the yield of wheat this year as compared to last year’s (and the reasons associated with it) or if a financial company wants to classify its customers based on their creditworthiness (before granting loans) or whether a retail organization wants to rewards extra points to its loyal customers, all need data scientists to process large volume of both structured and unstructured data in order to take crucial business decisions.
The main challenge that today’s Data Scientists face is not to find solutions to the existing business problems but to identify the problems that are most crucial to the organization and its success.
Why Data Scientists are called ‘Data Scientists’?
The term “Data Scientist” has been coined after considering the fact that a Data Scientist draws a lot of information from the scientific fields and applications whether it is statistics or mathematics. They make a lot of use of the latest technologies in finding solutions and reaching conclusions that are crucial for an organization’s growth and development. Data Scientists present the data in a much more useful form as compared to the raw data available to them from structured as well as unstructured forms.
Just like any other scientific discipline, data scientists always need to ask and find answers of What, How, Who and Why of the data available to them. They are required to make a clear defined plan and work towards achieving the results within limited time, effort and money.
Three components of Data Science:
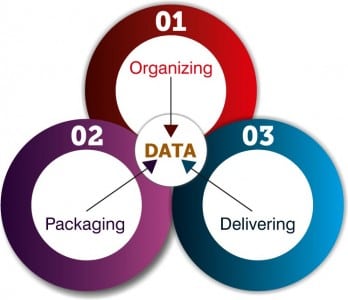 Data science consists of three components, that is, organizing, packaging and delivering data (OPD of data). Let’s have a brief look into these:
Data science consists of three components, that is, organizing, packaging and delivering data (OPD of data). Let’s have a brief look into these:
1. Organizing the data:
Organizing is where the planning and execution of the physical storage and structure of the data takes place after applying the best practices in data handling.
2. Packaging the data:
Packaging is where the prototypes are created, the statistics is applied and the visualisation is developed. It involves logically as well as aesthetically modifying and combining the data in a presentable form.
3. Delivering the data:
Delivering is where the story is narrated and the value is received. It makes sure that the final outcome has been delivered to the concerned people.
Data Science Training
What skills does a Data Scientist possess?
Role of a Data Scientist is indeed a challenging one! Though the skill-sets and competencies that Data Scientists employ differ extensively, to be an efficient Data scientist, he should:
- Be very innovative and distinctive in his approach in applying various techniques intelligently to extract data and get useful insights in solving business problems and challenges.
- Have the ability to locate and construe rich data sources.
- Have a hands-on experience in Data mining techniques such as graph analysis, pattern detection, decision trees, clustering or statistical analysis.
- Develop operational models, systems and tools by applying experimental and iterative methods and techniques.
- Analyze data from a variety of sources and perspectives and find out hidden insights.
- Perform Data Conditioning – that is, converting data into a useful form by applying statistical, mathematical tools and predictive analysis.
- Research, analyze, execute, and present statistical methods to gain practical insights.
- Manage large amounts of data even during hardware, software and bandwidth limitations.
- Create visualizations that will help anyone understand the trends in data analysis with ease.
- Be a team leader and communicate effectively with other business analysts, product Managers and Engineers.
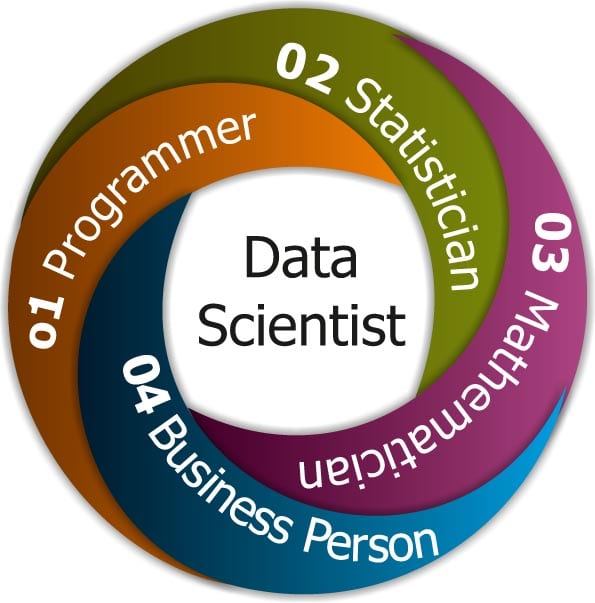
In brief, a Data Scientist should be very strong in any of these skills (Programming, Statistics, Mathematics, Business skills) and at the same time have a working-knowledge of the related skill-sets. For instance, a person with strong statistics background can become a data scientist while acquiring substantial skills in coding and business.
A Data Scientist is like a webmaster, who not only needs to be a jack of all trades but also a master of atleast one of the above fields.
So, what does a Data Scientist do?
A data scientist has a dual role – that of an “Analyst” as well as that of an “Artist”! Data scientists are very curious, who love a large amount of data, and more than that, they love to play with such huge data to reach important inferences and spot trends! This is what distinguishes a Data Scientist from a traditional Data Analyst. A Data scientist not only refers one particular source such as a social media site or a log file but various other sources with the aim to find out a hidden insight that can prove to be very significant for the organization. They perform “what if” analysis, ask questions and look at the data from different angles and transform the big data into the next Big idea!
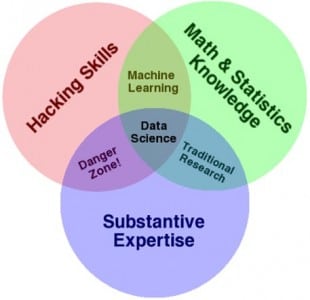
Conway Diagram:
This is the Conway Venn Diagram on Data Science illustrated by the famous Data Scientist Drew Conway. This diagram presents Data science as a combination of much-in demand skills such as hacking skills, math skills and knowledge of statistics including substantive expertise.
Data Science is also an Art!
Data science is not only a science or a technique, it is also an ‘Art’. Data Science is an art of listening to your intuitions while facing huge amount of data, classifying it, evaluating it and reaching conclusions. Not everyone is blessed with this art! Data scientists need to be really creative in visualizing the data in various graphical forms and present the highly complex data in a very simple and friendly way! If a Data scientist is able to convert terrifying Petabytes of structured as well as unstructured data (images, videos, log files, etc) into very easy and simple format, he is an – ‘Artist’!
After all only a skilful Data Scientist can manage McDonald’s Database or videos uploaded on Youtube, or Tesco’s huge volume of data or GE’s Healthcare data or managing the data related to thousands blood samples of patients at Apollo or unstructured data generated from X-rays!
Data Scientist Jobs
“US faces shortage of 140,000 to 190,000 people “with deep analytical skills, as well as 1.5 million managers and analysts with the know-how to use the analysis of big data to make effective decisions.”
– Mckinsey Global Institute
As Data Science is an emerging field, there is a plethora of opportunities available world across.
Just browse through any of the job portals; you will be taken aback by the number of job openings available for Data scientists in different industries, whether it is IT or healthcare, retail or Government offices or academics, life sciences, oceanography, etc. Venture Capitalists have never showed such an excitement in investing money as in the case of data driven start-ups.
Data Scientist Salary:
Below you can find very lucrative pay-packets offered to Data scientists!
Whether you call them Data scientists or Data Gurus or by some other fancy name, the fundamentals remain the same! The world is in acute need of smart and creative people who can dive deep inside the ocean of Big Data and save the world from ignorance and provide valuable insights into businesses and help the World Economy grow!

Edureka has a specially curated Data Science course which helps you gain expertise in Machine Learning Algorithms like K-Means Clustering, Decision Trees, Random Forest, Naive Bayes. You’ll learn the concepts of Statistics, Time Series, Text Mining and an introduction to Deep Learning as well. New batches for this course are starting soon!!
Trending Courses in Data Science
Browse Categories
https://analyticstwitter.blogspot.com/2023/07/the-top-21-data-engineering-interview.html
https://analyticstwitter.blogspot.com/2023/07/the-top-10-data-analytics-careers.html
https://analyticstwitter.blogspot.com/2023/07/5-types-of-binary-tree-explained.html
https://smartlifegadgets.shop/3-in-1-magnetic-wireless-fast-charger/
https://smartlifegadgets.shop/3-in-1-quick-car-ceramic-coating-spray/
https://smartlifegadgets.shop/3d-led-illusion-wall-lamp/
https://smartlifegadgets.shop/3d-pin-art/
https://itexamtools.com/top-100-startup-courses-and-mcqs/
https://itexamtools.com/top-100-advertising-strategy-courses-and-mcqs/
https://itexamtools.com/top-100-marketing-strategy-courses-and-qa/
https://itexamtools.com/top-100-tensorflow-courses-and-mcqs/
https://itexamtools.com/top-100-neural-networks-courses-and-qa/
https://itexamtools.com/top-100-computer-vision-courses-qa/
https://itexamtools.com/top-100-pytorch-courses-and-mcqs/




Comments
Post a Comment